The Theory.
Adsorption.
Adsorption is the adhesion of atoms, ions or molecules from a gas, liquid or dissolved solid to a surface.[1] This process creates a film of the adsorbate on the surface of the adsorbent. This process differs from absorption, in which a fluid (the absorbate) is dissolved by or permeates a liquid or solid (the absorbent), respectively.[2] Adsorption is a surface-based process while absorption involves the whole volume of the material. The term sorptionencompasses both processes, while desorption is the reverse of it. Adsorption is a surface phenomenon.
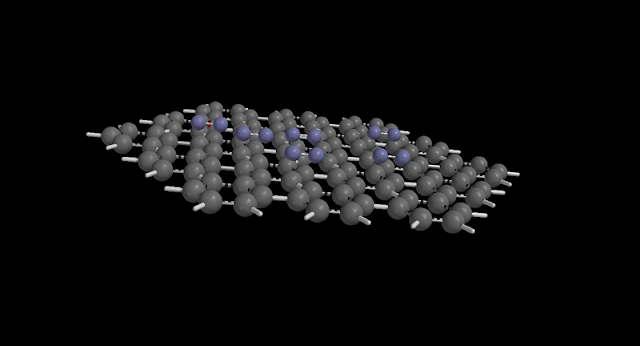 |
| The nitrogen gas molecules in blue adsorb onto the surface of a carbon nanotube in grey. |
IUPAC Definition
Increase in the concentration of a substance at the interface of a condensed and a liquid or gaseous layer owing to the operation of surface forces.
Note 1: Adsorption of proteins is of great importance when a material is in contact with blood or body fluids. In the case of blood, albumin, which is largely predominant, is generally adsorbed first, and then rearrangements occur in favor of other minor proteins according to surface affinity against mass law selection (Vroman effect).
Note 2: Adsorbed molecules are those that are resistant to washing with the same solvent medium in the case of adsorption from solutions. The washing conditions can thus modify the measurement results, particularly when the interaction energy is low.


Comments
Post a Comment